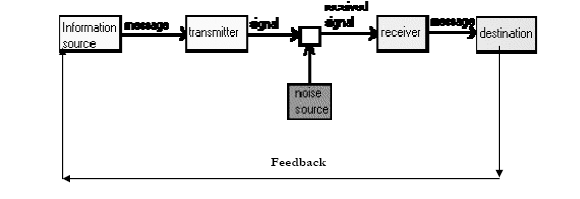
Feed back In its simplest form the feedback principle means that a behavior is tested with reference to its result and success or failure of this result influences the future behavior Though not exactly cut-out for human communication, the Shannon-Weaver model provides clear guidelines for researchers to mark more avenues for graphic presentation of the elements in daily human communication. Forms of feed back There are five main categories of feedback. They are listed in the order in which they occur most frequently in daily conversations. 1. Evaluation Making a judgment about the worth, goodness, or appropriateness of the sender’s statement. 2. Interpretation Paraphrasing – attempting to explain what the sender’s statement means. 3. Support Attempting to assist or support the sender. 4. Probing Attempting to gain additional information, continue the discussion, or clarify a point. 5. Understanding Attempting to discover completely what the sender means by his/her statement. Role […]
Five news stories that appeared in Urdu newspapers Translated in English
News Story No. 1 The Network for Consumer Protection has expressed concern at the dramatic increase in sugar price and alleged that sugar barons having clout in the government have created an artificial shortage. Sugar price has surged to an all-time high of Rs120 per kg in a week from Rs85 on Oct 31, proving that the government has miserably failed to keep a check on food prices and provide relief to consumers, a press release issued by the organisation said on Tuesday. Its executive coordinator, Dr Arif Azad, said roots of the problem lay in the sugar lobby’s political clout in determining sugar output, timing of import and scaremongering about rises in prices. “For the sake of protecting consumers from artificially inflated sugar price rises, the government has to bring in regulatory measures to rein in the power of sugar lobby,” he said. He called for an investigation to […]
Guidelines of precis writing
It was not so in Greece, where philosophers professed less, and undertook more. Parmenides pondered nebulously over the mystery of knowledge; but the pre-Socratics kept their eyes with fair consistency upon the firm earth, and sought to ferret out its secrets by observation and experience, rather than to create it by exuding dialectic; there were not many introverts among the Greeks. Picture Democritus, the Laughing Philosopher; would he not be perilous company for the desiccated scholastics who have made the disputes about the reality of the external world take the place of medieval discourses on the number of angles that could sit on the point of a pin? Picture Thales, who met the challenge that philosophers were numskulls by “cornering the market” and making a fortune in a year. Picture Anaxagoras, who did the work of Darwin for the Greeks and turned Pericles form a wire-pulling politician into a thinker […]
Differences between journalistic and literary writing
Journalistic writing Joseph Pulitzer, a famous publisher in the 1800s, stressed one of the most important qualities of journalistic writing in his memorable command: “ Accuracy! Accuracy! Accuracy!” Roger Mudd’s quote on the first slide refers to another important quality of journalistic writing: objectivity. In addition, all journalistic writing should be clear, concise and colorful. Nothing is more embarrassing or unprofessional than writing and publishing a story that has factual inaccuracies. As a reporter, we were responsible for the information printed in your story. Review everything carefully. Our reputation, and that of your publication, is at stake. Double-check the spellings of student, faculty, and staff names, as well as grade levels and titles. Refer to official documents listing this information, such as homeroom lists or a school directory. Keep a current phone book and an atlas handy to double-check the names of organizations and places. Double-check dates, using a calendar […]
Uses and Gratifications Approach
Uses and Gratifications One influential tradition in media research is referred to as ‘uses and gratifications’ (occasionally ‘needs and gratifications’). This approach focuses on why people use particular media rather than on content. In contrast to the concern of the ‘media effects’ tradition with ‘what media do to people’ (which assumes a homogeneous mass audience and a ‘hypodermic’ view of media), U & G can be seen as part of a broader trend amongst media researchers which is more concerned with ‘what people do with media’, allowing for a variety of responses and interpretations. However, some commentators have argued that gratifications could also be seen as effects: e.g. thrillers are likely to generate very similar responses amongst most viewers. And who could say that they never watch more TV than they had intended to? Watching TV helps to shape audience needs and expectations. U & G arose originally in the 1940s and underwent a revival […]
Different forms of Journalistic writing
There are following different forms of Journalistic writing the details is as under 1. News writing News writing follows a basic formula; there are key elements every news story follows. While styles can diverge more dramatically depending on the kind of story a feature story may look and sound very different than a hard news one all news stories are cut from the same mold. The first element of news writing is, of course, to deliver the news. Most people have heard of the 5 W’s, even if they’ve never taken a journalism class. The W’s in question, as you probably know, refer to the Who, What, When, Where and Why that every story should address. Depending on what the story is, how and when you answer those W’s may change. If, for example, you’re reporting on a drive-by shooting in a city, we likely start with where the crime […]